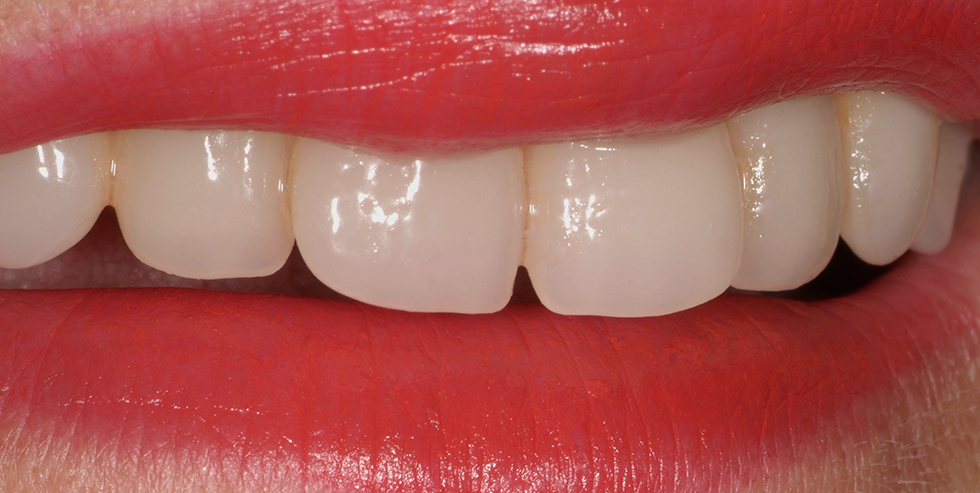
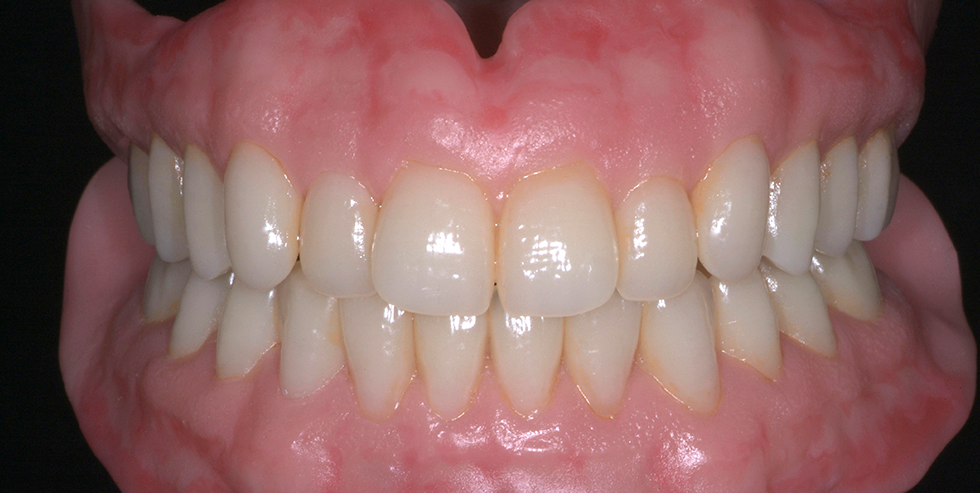
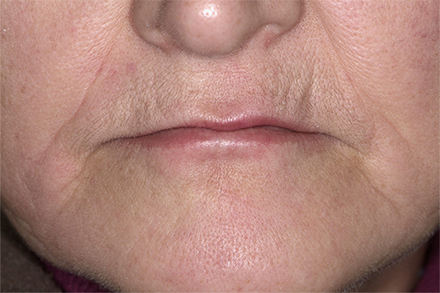
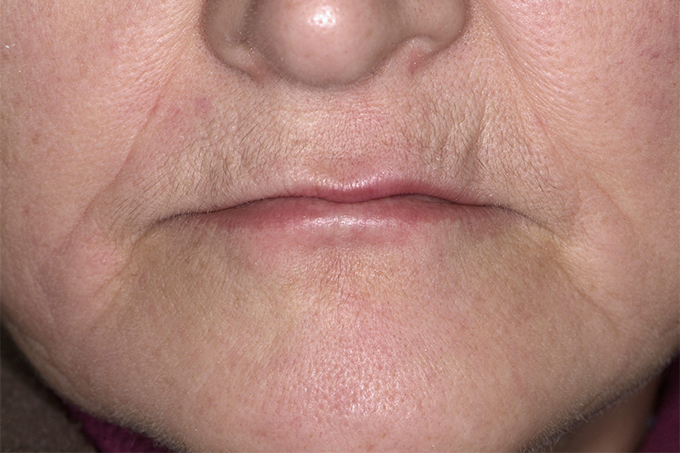
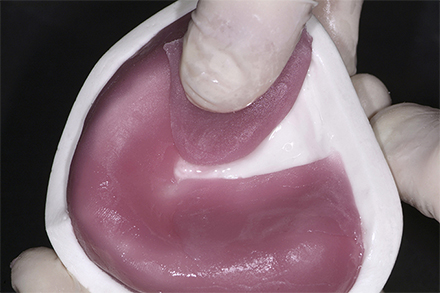
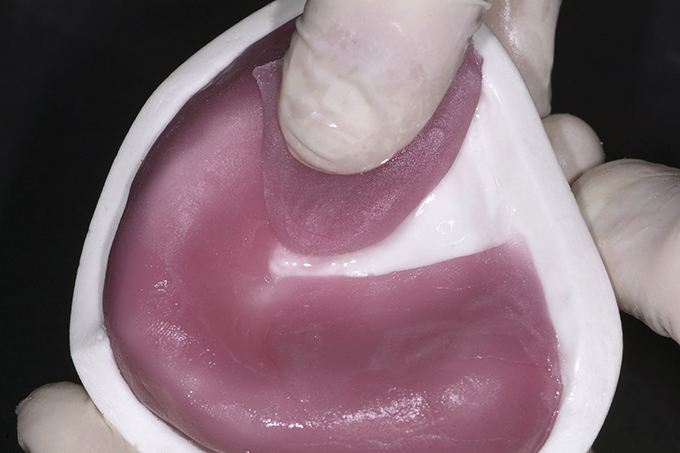
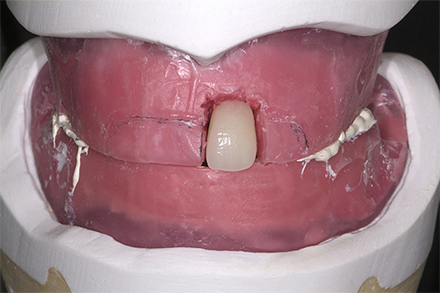
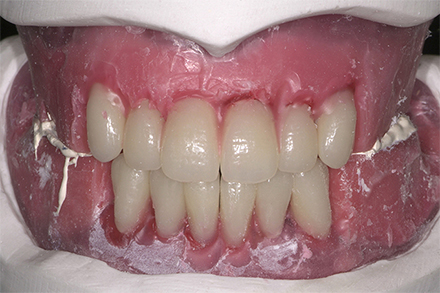
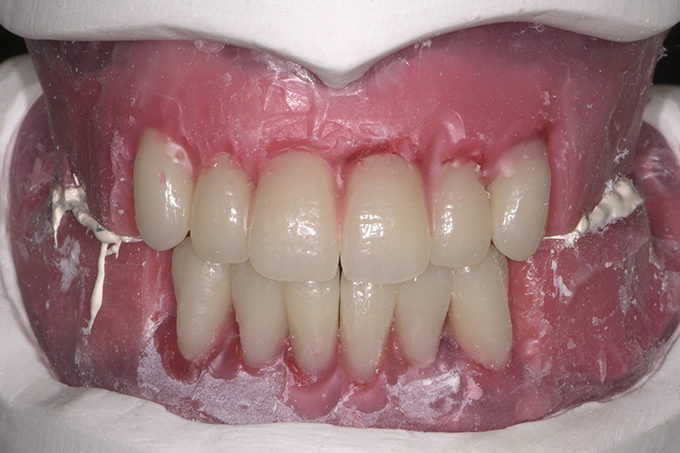
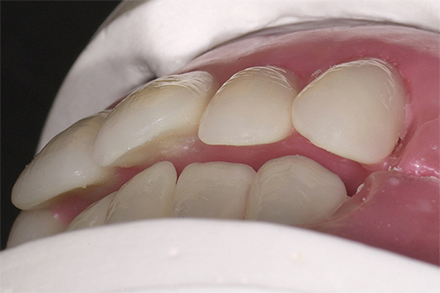
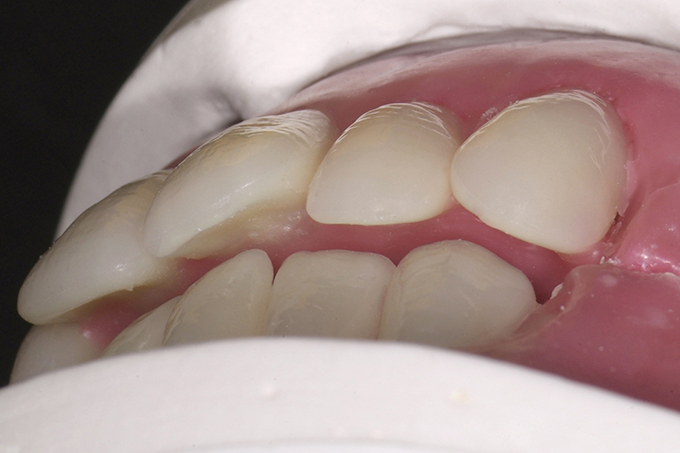
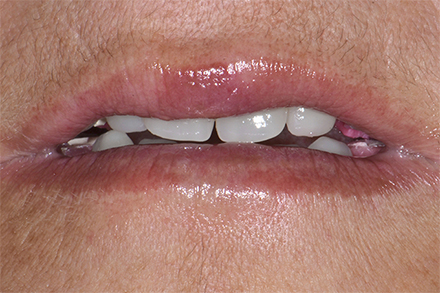
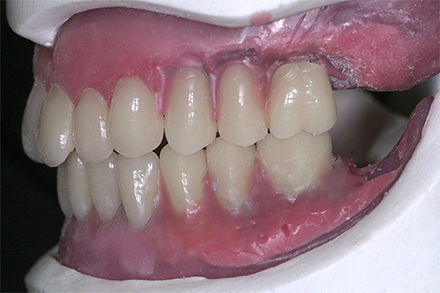
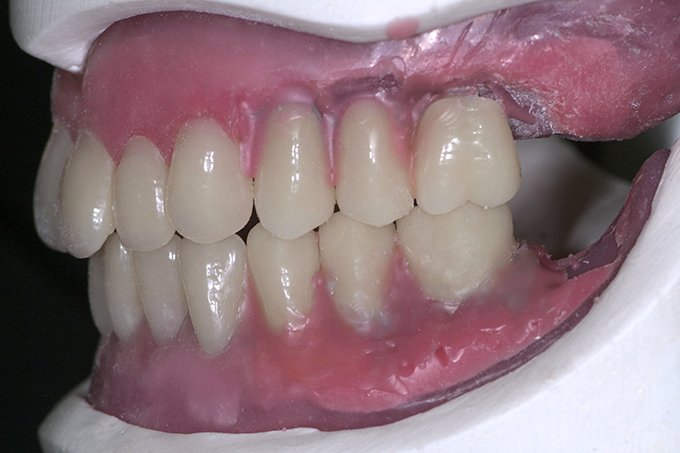
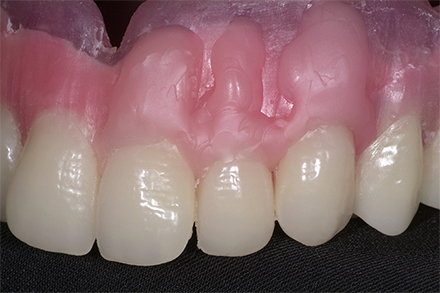
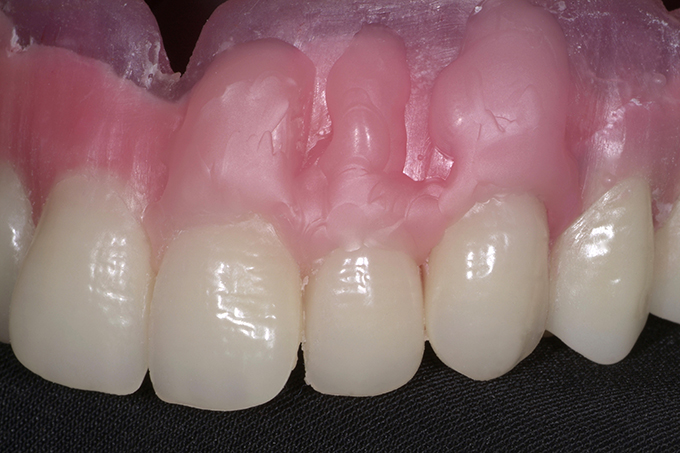
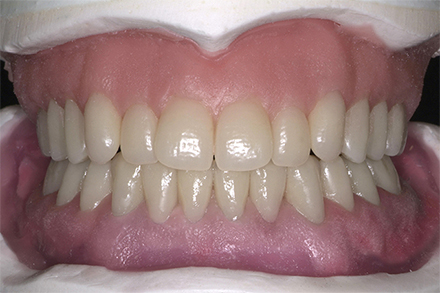
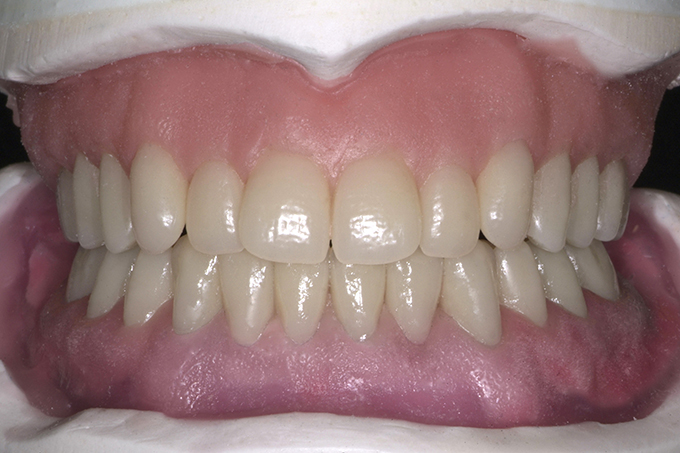
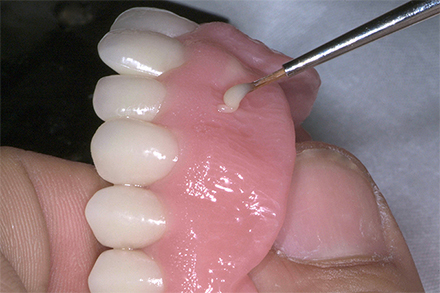
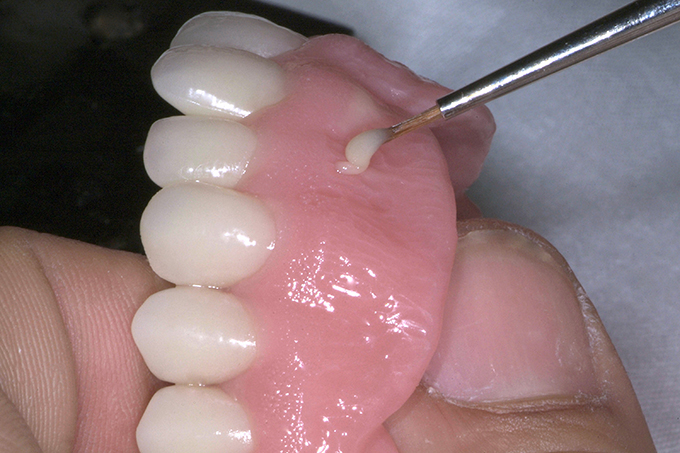
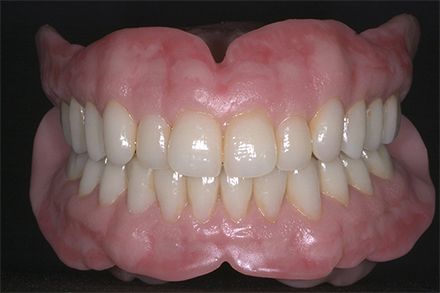
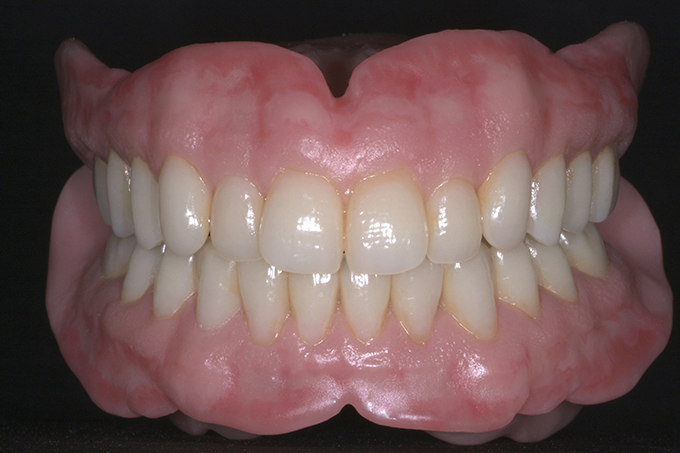
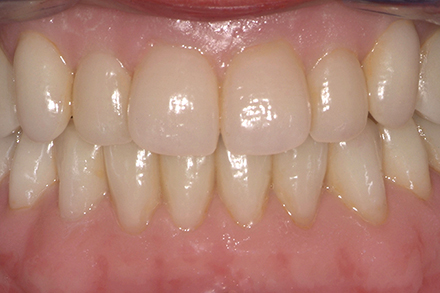
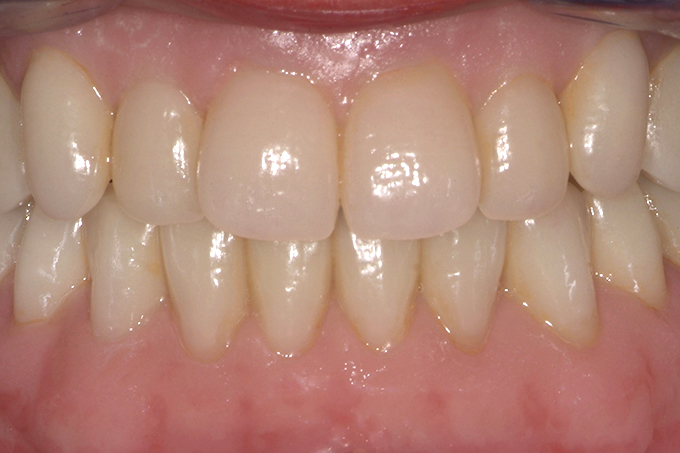
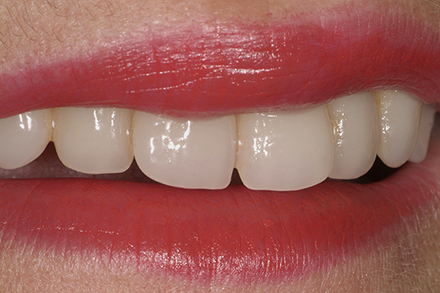
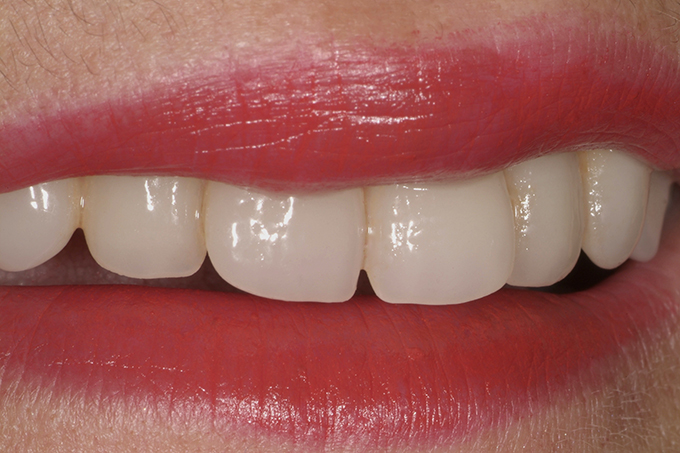
The patient, a 58-year-old woman, presented in our practice. Her medical history indicated satisfactory general health. During the clinical examination, the practitioner identified difficulties in function and speech that had had a negative impact on her social relationships. The patient wanted complete restoration of the oral situation. The goal of restoration was the fabrication of full dentures that would offer optimum esthetics in addition to perfect function.
 It appears that you are currently in United States.
It appears that you are currently in United States.